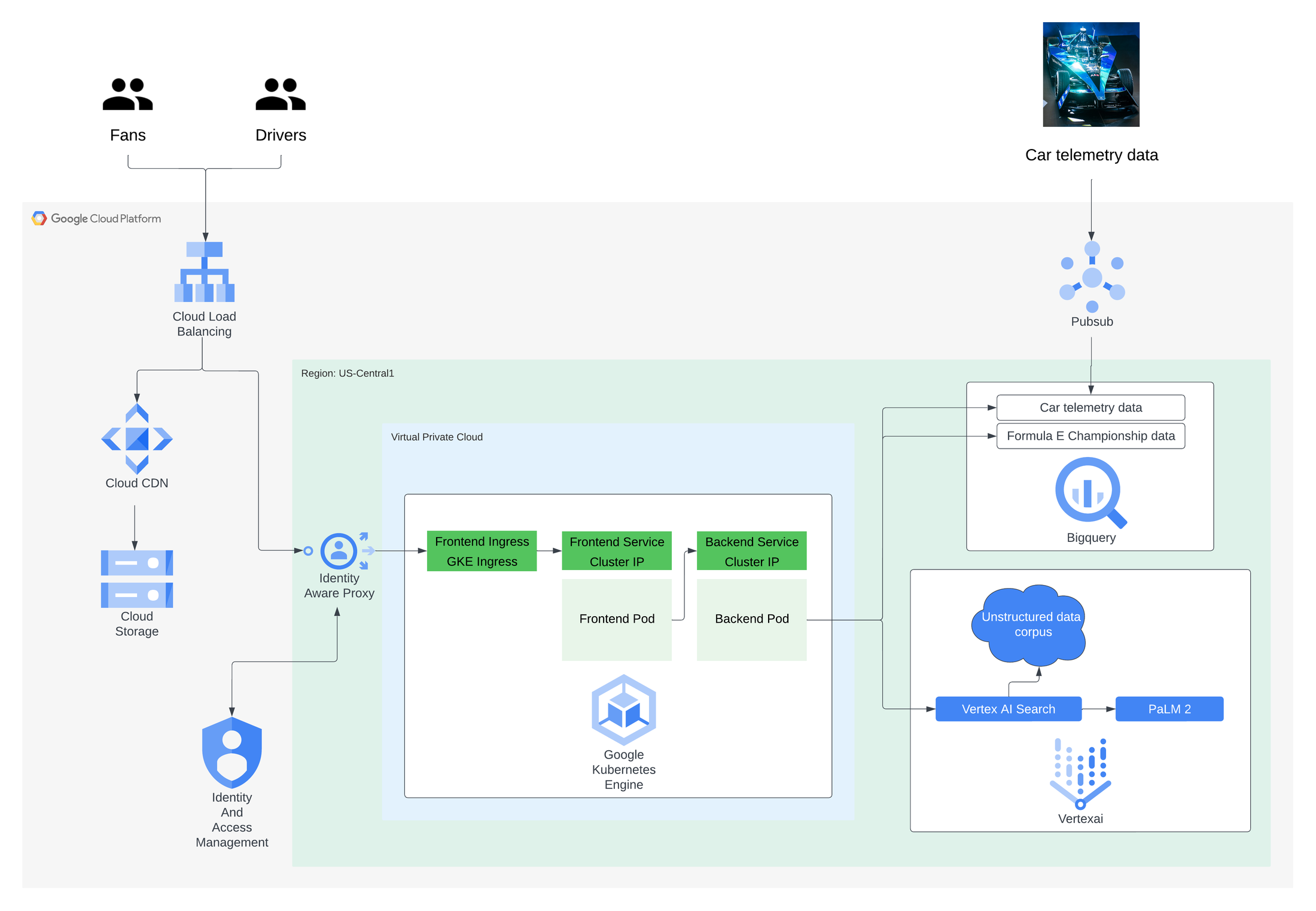
The backend service is where the gen AI logic resides. It uses Google's
PaLM 2 API for chat available in
Vertex AI to provide a general-purpose conversational framework as a base-layer. Above this, additional context is provided to enable more tailored and context-rich responses:
- Structured data such as car telemetry data and historical championship results
- Unstructured text corpus including general information on Formula E and information to differentiate Formula E from other motorsports
Adding context from structured data using a combination of BigQuery, Vertex AI and LangchainFormula E has a lot of structured data that is very relevant to both drivers and fans, so wanted this additional data to be part of responses. This includes data from previous and current championships such as race results and qualifying times, as well as very granular telemetry data coming from sensors all over the race cars. Batch uploading and
streaming this data to
BigQuery was the first step in allowing the backend service to access this information and augment its responses with insights found in the data.
The next step was for the backend to dynamically query these datasets that sit outside the foundational model’s training set to retrieve the additional information it requires to more precisely answer the user’s questions.
Langchain is an open-source framework for language models and
includes a way to dynamically generate SQL based on an input question, and only requires coaching through prompt tuning rather than any fine-tuning on the data itself. By using Langchain with Google's PaLM 2 API for text available in
Vertex AI , the backend service can first identify the sorts of questions that would require additional data from the structured datasets. Then a SQL query is dynamically generated that queries the relevant BigQuery tables to return the relevant data to answer the question and return this back to the frontend.
For example, a question such as “Who won the race in Rome in the 2018 season?” would be identified as a question sitting outside the foundational model’s training set and would be better answered by querying the structured data that exists for race results. A query similar to the below example would be dynamically constructed and ran against the relevant BigQuery table, returning the requested name of the driver, which can then be sent back to the frontend:
SELECT drivername FROM race_data WHERE season = 4 AND racename = 'Rome' AND session = "ses_v-race" AND pos = 1
Adding context from unstructured data with Vertex AI SearchVertex AI Search is a gen AI offering from Google Cloud that helps enable a Google Search-style experience across a specified corpus of structured, unstructured or website-based data sources.
Formula E added a wide range of unstructured information to Vertex AI Search, covering what Formula E is, its commitment to sustainability, information on previous, current and future generation race cars, and many other topics. When a question is received by the backend service, it also determines whether it should first pass this question to Vertex AI Search, asking it to return the most relevant information from the unstructured data corpus.
After retrieving additional context-rich information from Vertex AI Search, this is then sent to the foundational model in addition to the original question. This provides the general-purpose PaLM 2 model with additional Formula E context to build a more specific and more relevant response before returning the answer back to the frontend.
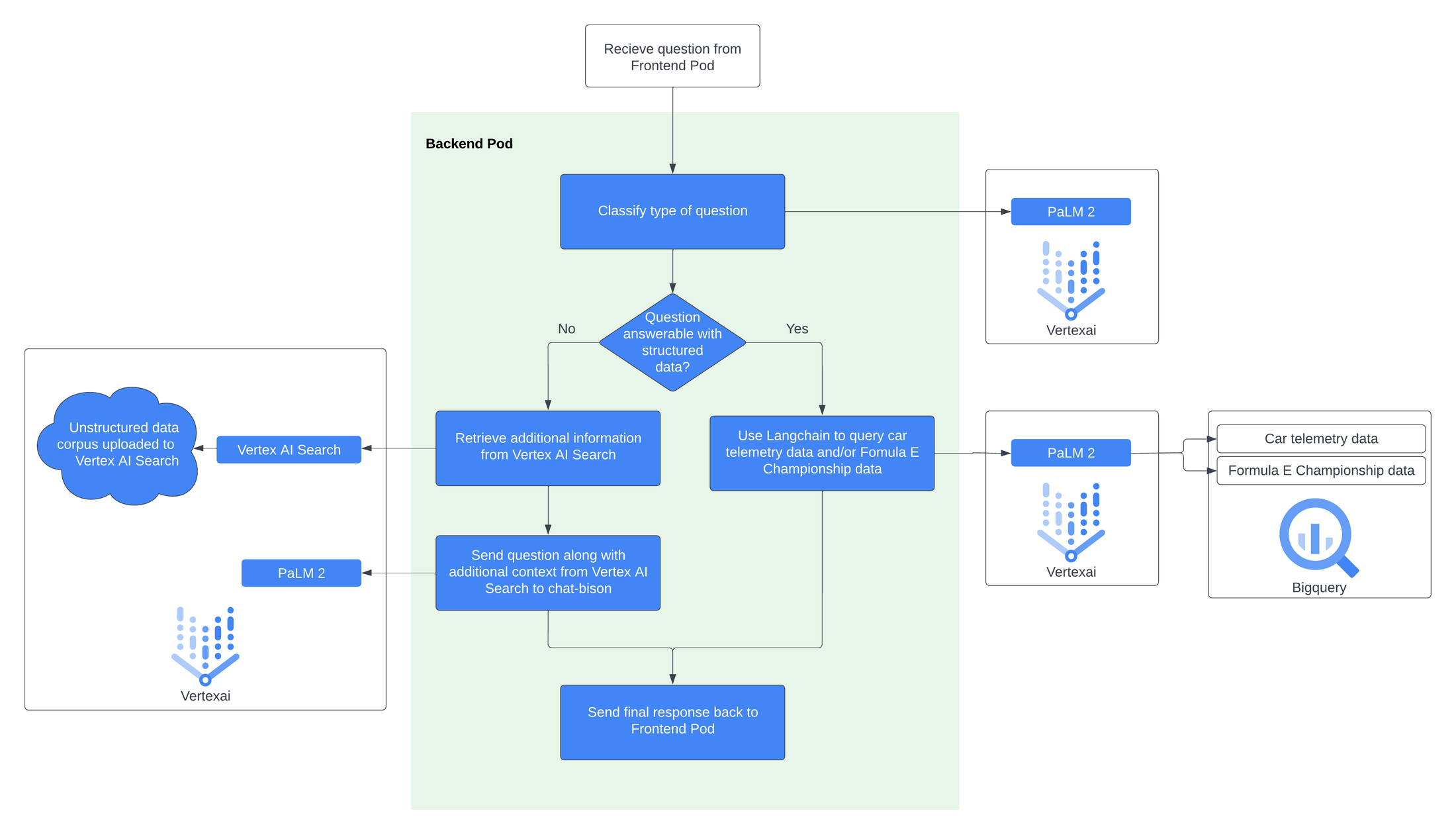
This following diagram represents the complete backend behavior visually: