For the past several years, we’ve been working alongside our partners to democratize earth-based data in Google Earth Engine so that it’s more accessible, usable, and actionable.
Streamlined geospatial integrationClimate Engine, a Google Cloud Ready Sustainability partner, has launched a solution called
SpatiaFi. By merging Earth and asset-location data, such as a farmer’s field or a highway, conditions can be monitored and analyzed in near-real time to understand the risks and impacts of climate events like floods or wildfires before, during, and after they occur. With the ability to analyze historical, current, near-term, and future time horizons, SpatiaFi helps organizations assess economic impacts as well as the sustainability and resilience of their operations.
Global weather forecasting with AILast month DeepMind shared
GraphCast, an AI model for faster and more accurate global weather forecasting. GraphCast can also offer early warnings of extreme weather events, accurately predicting the tracks of cyclones, identify “atmospheric rivers” associated with flood risk, or the onset of extreme temperatures. By enabling greater preparedness, GraphCast has the potential to save lives.
Leveraging LLMs and generative AIWith the explosion of AI this year we’ve seen technology change how we think about sustainability challenges, and the proliferation of tools such as geospatial AI to both screen data quality and verify ESG claims is putting more focus on this important issue.
Generative AI, too, is transforming the analytics landscape, enabling users of all technical abilities to navigate complex data.
CARTO, in particular, improves the accessibility of geospatial data with conversational GIS, allowing users of all levels to
replace complex analytics workflows with dialogue.
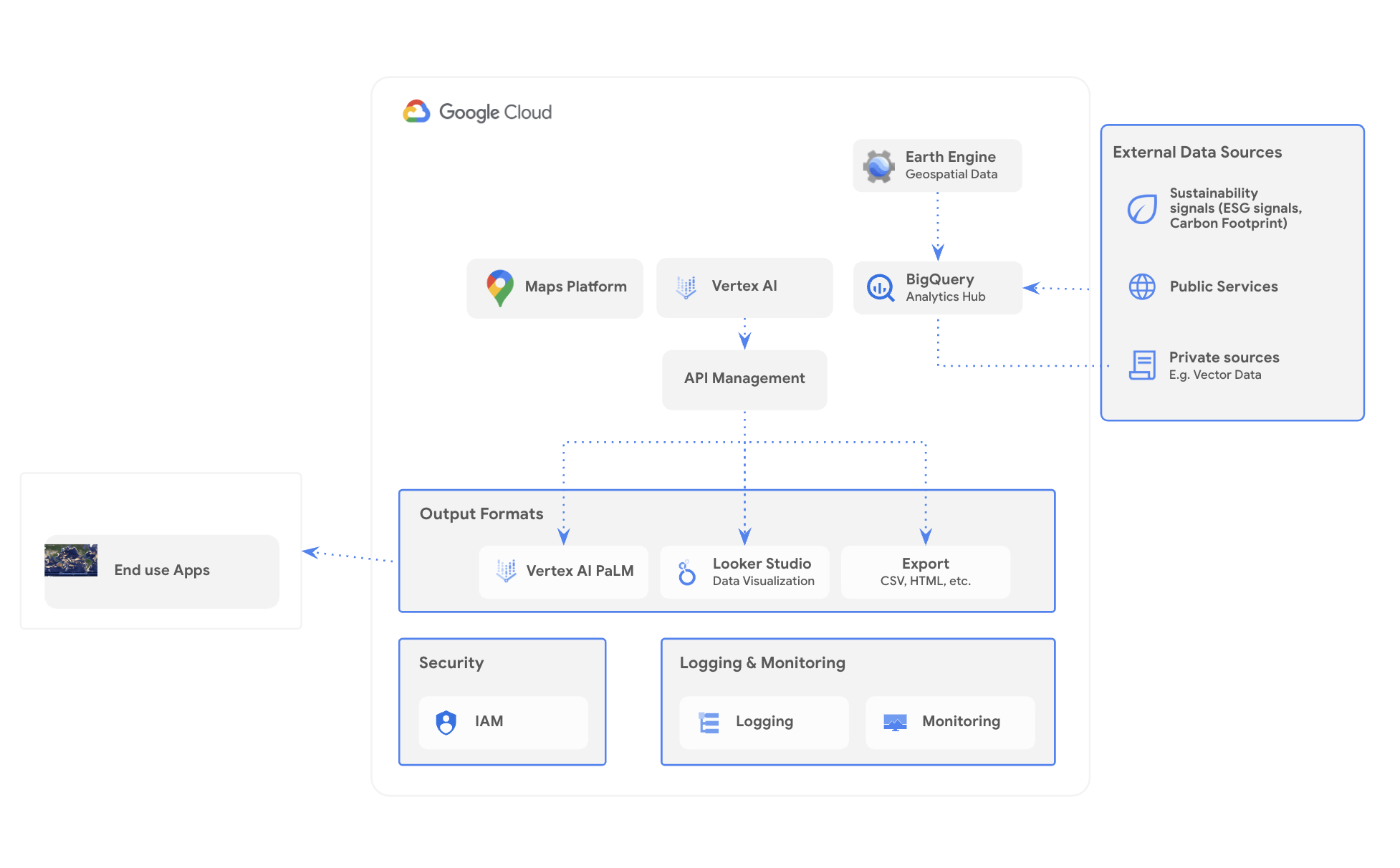 Example architecture of Geospatial Analytics on Google Cloud
Example architecture of Geospatial Analytics on Google Cloud